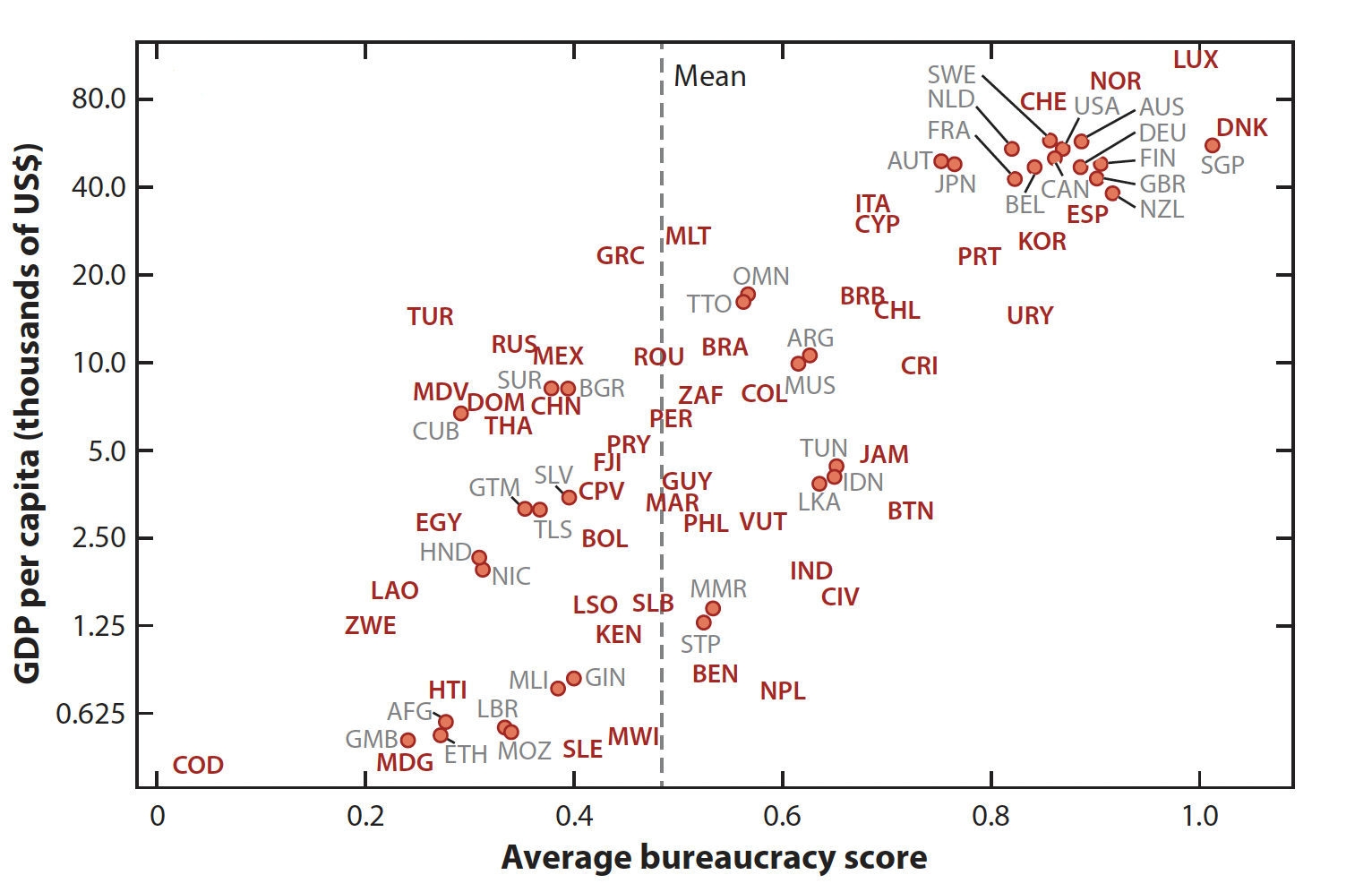
Political Economy
What impact do incentive structures have on the effectiveness of bureaucratic institutions? Under what conditions are politicians responsive to their citizen's needs and accountable to their voters? How can governments design reforms to improve economic outcomes?
Robin Burgess' work on political economy has been focused on ways to improve state capacity. He has worked with the government of India on tax system reform, and with the governments of Myanmar, India, and Pakistan on reforms of the energy sector.
Bureaucracy and Development
With Timothy J. Besley, Adnan Khan and Guo Xu
The Annual Review of Economics, 2022, 14: 397-424.
Abstract
Organization of the State: Home Assignment and Bureaucrat Performance
With Guo Xu and Marianne Bertrand
The Journal of Law, Economics and Organization, 2021
Abstract
Cycles of Fire? Politics and Forest Burning in Indonesia
With Clare Balboni, Anton Heil, Jonathan Old, and Ben Olken
The American Economic Association: Papers & Proceedings
Published Paper Online Appendix
Abstract
The Glittering Prizes: Career incentives and bureaucrat performance
With Guo Xu, Marianne Bertrand and Arunish Chawla
The Review of Economic Studies, 2020, 87(2): 626-655
Published Paper Online Appendix Replication Files
Press Coverage: ThePrint
Abstract
All related publications
Working Papers
- Railroads and the Demise of Famine in Colonial India
Robin Burgess and Dave Donaldson
2017, Working Paper.
Link to working paper
Published Papers
- Bureaucracy and Development
Timothy J. Besley, Robin Burgess, Adnan Khan and Guo Xu
2022, In: The Annual Review of Economics, 14: 397-424.
Link to publication - Organization of the State: Home Assignment and Bureaucrat Performance
Guo Xu, Marianne Bertrand, and Robin Burgess
2021, The Journal of Law, Economics and Organization.
Link to publication - Cycles of Fire? Politics and Forest Burning in Indonesia
Clare Balboni, Robin Burgess, Anton Heil, Jonathan Old and Benjamin A. Olken
2021, In: The American Economic Association: Papers and Proceedings.
Link to publication - The Glittering Prizes: Career Incentives and Bureaucrat Performance
Marianne Bertrand, Robin Burgess, Arunish Chawla, and Guo Xu
2020, In: The Review of Economic Studies, 87 (2): 626–655.
Link to publication - War and Deforestation in Sierra Leone
Robin Burgess, Edward Miguel, and Charlotte Stanton
2015, In: Environmental Research Letters, 10 (9): 095014.
Link to publication - The Value of Democracy: Evidence from Road Building in Kenya
Robin Burgess, Remi Jedwab, Edward Miguel, Ameet Morjaria, and Gerard Padró i Miquel
2015, In: American Economic Review, 105 (6): 1817–1851.
Link to publication - The Political Economy of Deforestation in the Tropics
Robin Burgess, Matthew Hansen, Benjamin A. Olken, Peter Potapov, and Stefanie Sieber
2012, In: The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 127 (4): 1707–1754.
Link to publication - The Unequal Effects of Liberalization: Evidence from Dismantling the License Raj in India
Philippe Aghion, Robin Burgess, Stephen Redding, and Fabrizio Zilibotti
2008, In: American Economic Review, 98 (4): 1397–1412.
Link to publication - Entry Liberalization and Inequality in Industrial Performance
Philippe Aghion, Robin Burgess, Stephen Redding, and Fabrizio Zilibotti
2005, In: Journal of the European Economic Association, 3 (2): 291–302.
Link to publication - Mass Media and Political Accountability
Timothy Besley, Robin Burgess, and Andrea Prat
2002, In: The Right to Tell : The Role of Mass Media in Economic Development, edited by Roumeen Islam, published by The World Bank. Pages 45–60.
Link to working paper - The Political Economy of Government Responsiveness: Theory and Evidence from India
Timothy Besley and Robin Burgess
2002, In: The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 117 (4): 1415–1451.
Link to publication - Political Agency, Government Responsiveness and the Role of the Media
Timothy Besley and Robin Burgess
2001, In: European Economic Review, 45 (4): 629–640.
Link to publication - Land Reform, Poverty Reduction, and Growth: Evidence from India
Timothy Besley and Robin Burgess
2000, In: The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 115 (2): 389–430.
Link to publication - The Reform of Indirect Taxes in India
Robin Burgess, Stephen Howes, and Nicholas Stern
1995, In: India, the Future of Economic Reform, edited by Robert Cassen and Vijay Joshi, published by Oxford University Press. Pages 113–166.
Link to book - Value-added tax options for India
Robin Burgess, Stephen Howes, and Nicholas Stern
1995, In: International Tax and Public Finance, 2 (1): 109–141.
Link to publication - The Behaviour of State Firms in Eastern Europe, Pre-Privatisation
Philippe Aghion, Olivier Blanchard and Robin Burgess
1994, In: European Economic Review, 38 (6): 1327–1349.
Link to publication - Taxation and Development
Robin Burgess and Nicholas Stern
1993, In: Journal of Economic Literature, 31 (2): 762–830.
Link to publication
Other papers
- Benchmarking Government Provision of Social Safety Nets
Timothy Besley, Robin Burgess, and Imran Rasul
2003, Social Protection Discussion Papers and Notes 27870, The World Bank.
Link to working paper